Industry News
Axle basics
Writer: Admin Time:2021-04-20 Browse:1776℃
The drive axle is the mechanism at the end of the drive train that changes the speed and torque from the transmission and transmits them to the drive wheels.

▲The powertrain is longitudinally placed, and the power output from the transfer case is transmitted to the front drive axle.
The drive axle is generally composed of a final drive, a differential, a wheel drive and a drive axle housing, and the steering axle has a constant velocity joint.
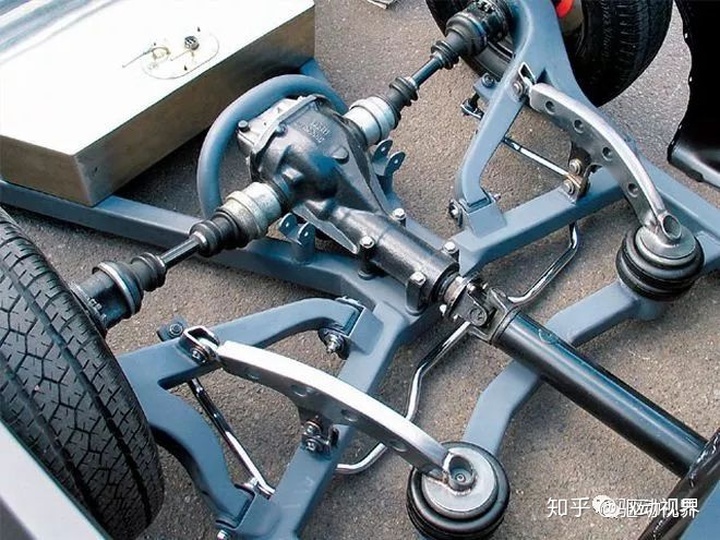

▲Disconnected (independent suspension) drive axle, consisting of a final drive and a constant speed drive shaft
In addition, the transaxle is also subjected to vertical forces, longitudinal and lateral forces acting on the road surface and the frame or body, as well as braking torque and reaction forces.
The car axle (also known as the axle) is connected to the frame (or the load-bearing body) through the suspension, and the wheels are mounted at both ends. The role of the axle is to withstand the load of the car and maintain the normal driving of the car on the road.
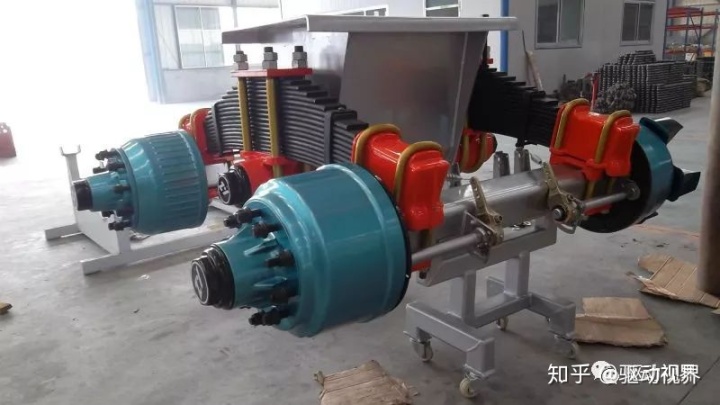

▲The trailer bridge is also called the axle in a broad sense.
The axle can be integral, like a huge barbell, and the two ends support the body through the suspension system, so the integral axle usually cooperates with the non-independent suspension; the axle can also be disconnected, like two The umbrellas are inserted on both sides of the body, and each supports the body through the suspension system, so the disconnected axle is used with the independent suspension.
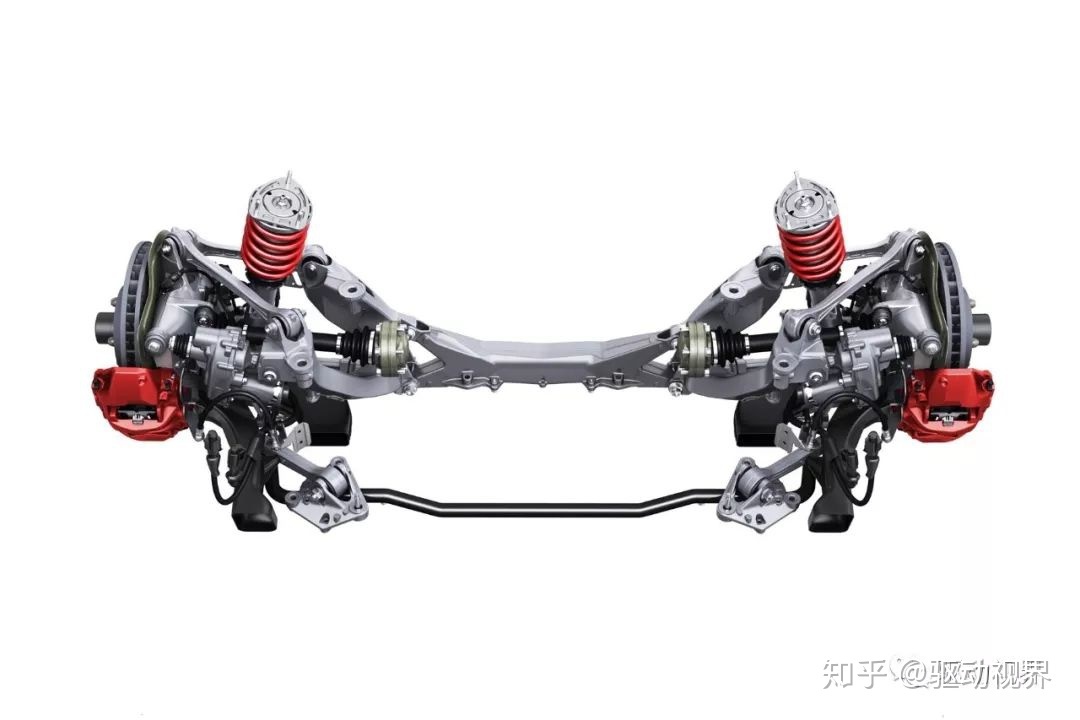

▲Foreign passenger car, its gearbox is actually composed of three parts: transmission, reducer and differential. The reducer and differential that belonged to the transaxle are integrated into the gearbox, so there is no axle in the conventional sense.
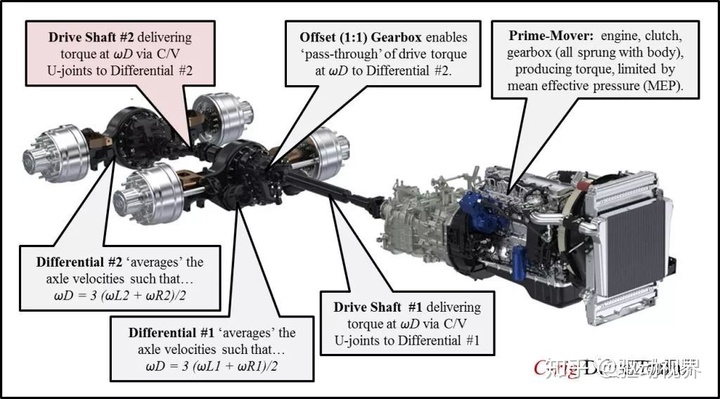
▲Typical powertrain, engine + transmission + drive axle
According to different driving methods, axles are also divided into four types: steering axle, drive axle, steering axle and support axle. The steering axle and the support bridge are both driven bridges. Most cars use a front-mounted rear drive (FR), so the front axle acts as a steering axle and the rear axle acts as a drive axle; while the front-front drive (FF) car has a front axle that becomes a steering axle and the rear axle acts as a support bridge.
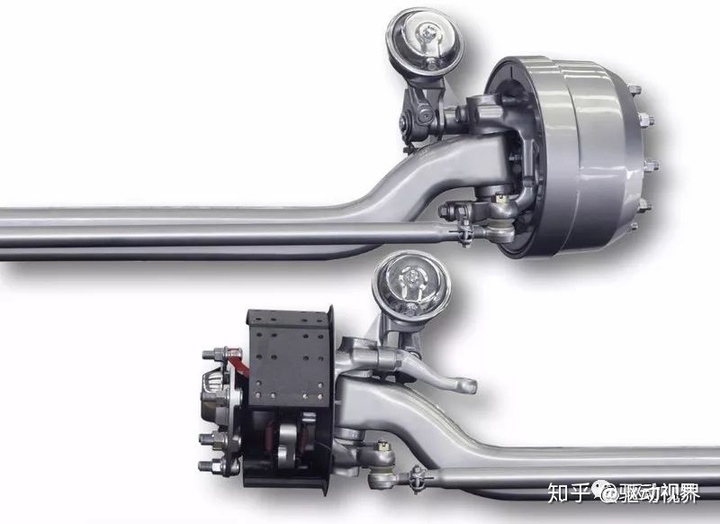
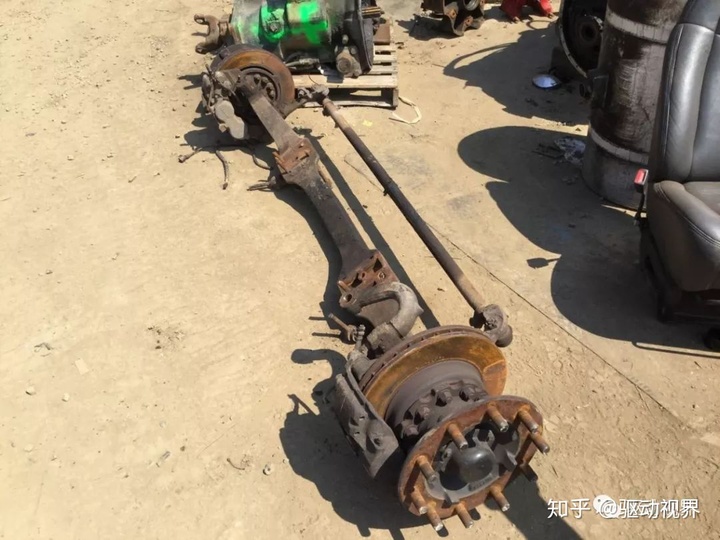
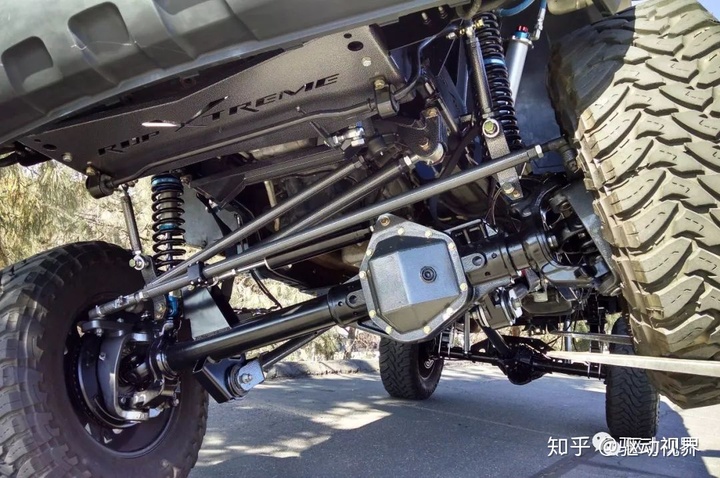
The front axle is mostly a driven bridge, also known as a steering axle. It is generally distributed at the front end of the vehicle, so it is called the front axle. It uses a steering knuckle to connect to the steering system. The steering force output from the steering gear can be transmitted to the wheels to achieve steering of the vehicle. It not only supports the sprung mass at the front of the vehicle, but also withstands vertical loads and various longitudinal forces, lateral forces and associated moments.
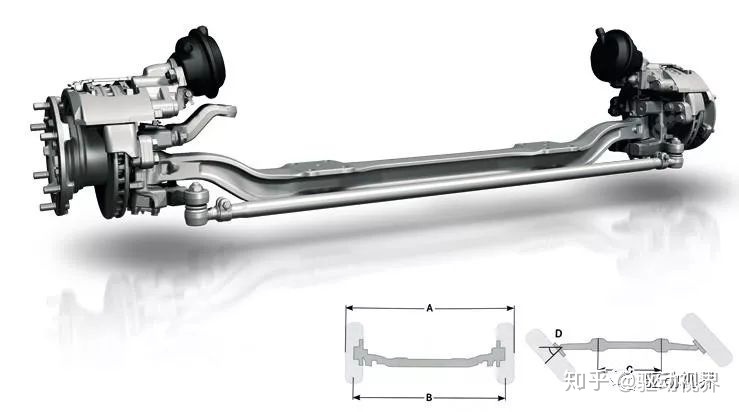
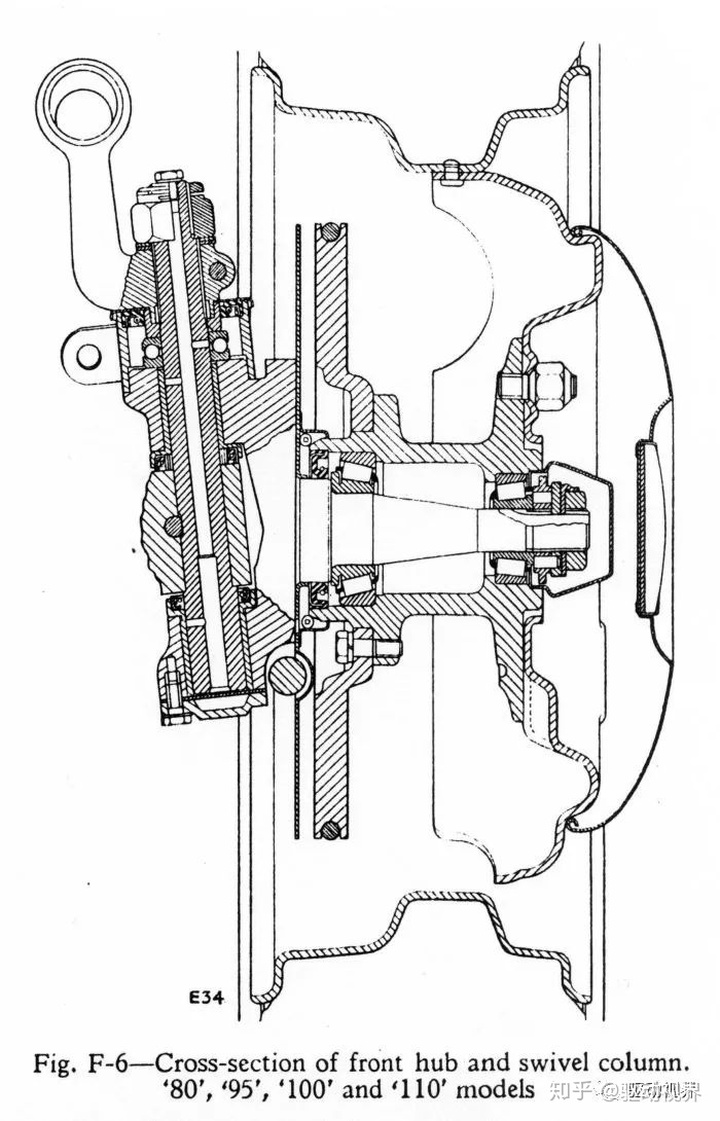
The steering axles of various types of vehicles are basically the same, mainly composed of front axles (beams), steering knuckles, kingpins and hubs, brakes, etc.
As the front shaft of the main part, it is generally made of medium carbon steel by die forging and heat treatment. Its section is I-shaped or tubular, as shown.

In order to improve the torsional strength, there is a thickened portion at each end near the front shaft into a fist shape, in which a through hole is inserted, and the king pin is inserted into the hole. The central portion is curved downwardly into a concave shape for the purpose of reducing the position of the engine, thereby reducing the center of mass of the vehicle; expanding the driver's field of view; and reducing the angle between the drive shaft and the output shaft of the transmission.
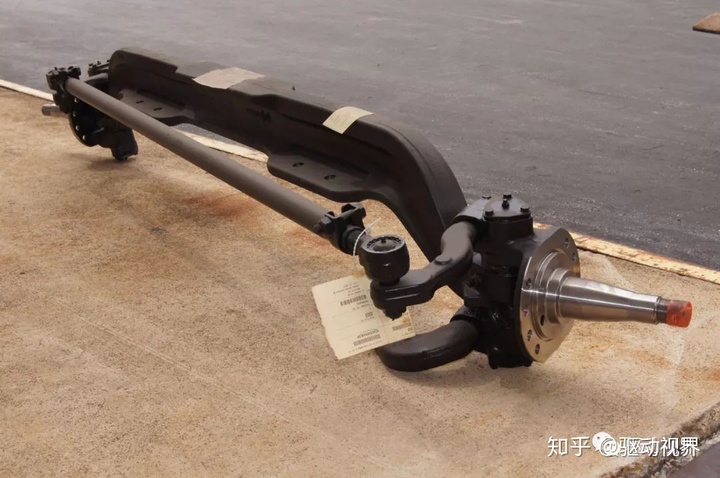

The steering knuckle is the hinge of the wheel steering, which is a fork. The upper and lower forks have two coaxial holes for mounting the kingpin, and the knuckle journals are used to mount the wheels. The two ears of the knuckle pin hole are connected to the fist portion at both ends of the front axle through the king pin, so that the front wheel can be deflected by a certain angle around the king pin to steer the car.

In order to reduce wear, the bronze bushing is pressed into the knuckle pin hole, and the lubrication of the bushing is lubricated with a grease fitting attached to the knuckle. In order to make the steering flexible, a bearing is arranged between the lower part of the knuckle and the front part of the front axle. An adjustment spacer is also placed between the upper ear and the glove portion of the steering knuckle to adjust the gap therebetween.

The function of the kingpin is to articulate the front axle and the steering knuckle, so that the steering knuckle swings around the kingpin to achieve steering of the wheel. The middle of the kingpin is cut with a groove, and the main pin fixing bolt 5 is engaged with the groove on the upper side of the main pin to fix the king pin in the punch hole of the front axle. The king pin is mated with the pin hole on the steering knuckle for steering.

The wheel hub is supported by the two tapered roller bearings on the journal at the outer end of the knuckle. The tightness of the bearing can be adjusted with an adjustment nut (mounted on the outer end of the bearing). The outer end of the hub is covered with a stamped metal cover and the inner end is fitted with an oil seal. The brake shoe and the dust cover are fixed to the steering knuckle together.
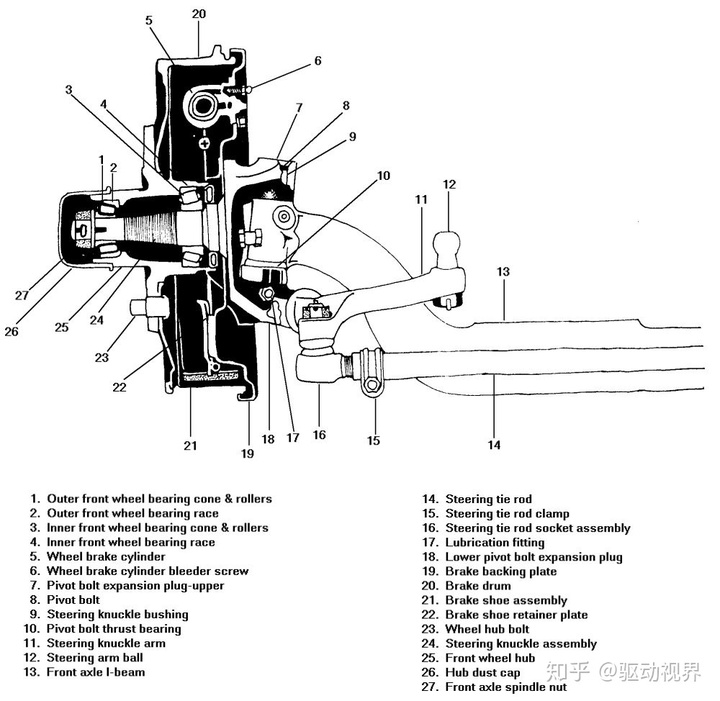
Front bridge sectional view
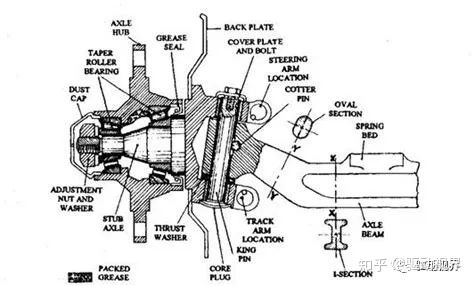
Front bridge sectional view
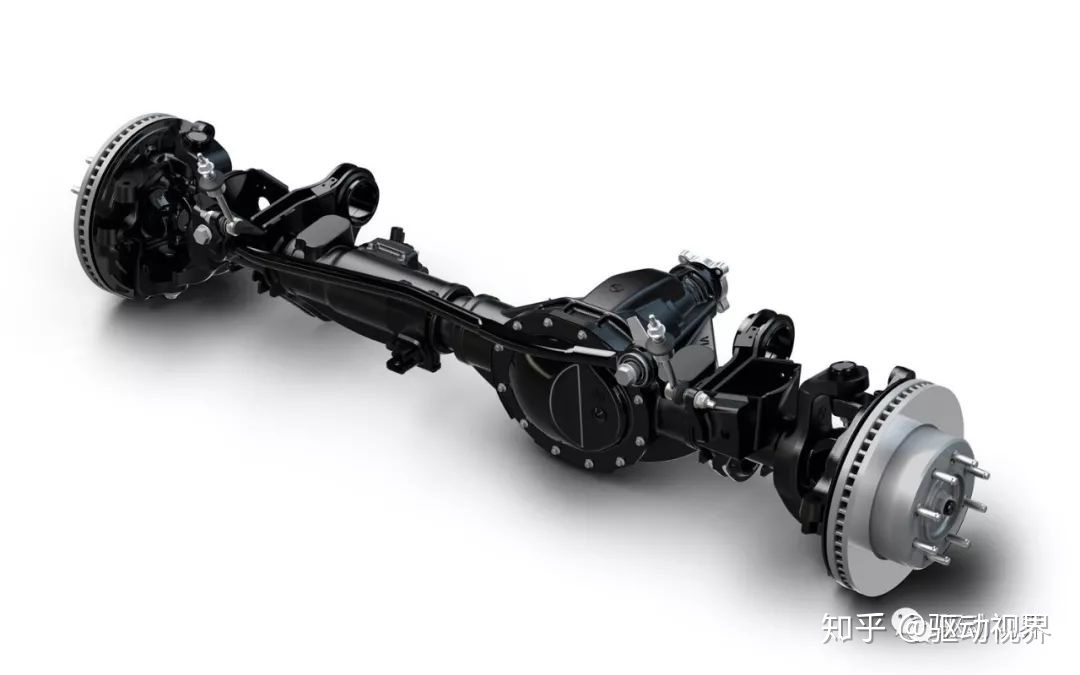

Front axle section view In many cars and all-wheel-drive off-road vehicles, the front wheel is used as a steering axle in addition to the steering axle, so it is called a steering axle.

The steering axle has both the final drive, the differential and the half shaft of the general drive axle; it also has the knuckle housing, the king pin 1 and the hub of the general steering axle.

Compared with the separate drive axle and steering axle, the difference is that the half shaft is divided into two sections due to the need of steering, namely the inner half shaft (connected to the differential) and the outer half shaft (with the hub). Connect), the two are connected by an equiangular velocity joint.

At the same time, the kingpin is thus divided into upper and lower sections, which are respectively fixed on the spherical bearings of the universal joint. The knuckle journal is hollowed so that the outer half shaft passes therethrough. The connecting fork of the steering knuckle is a spherical steering knuckle housing, which not only meets the needs of steering, but also adapts to the transmission force of the steering knuckle. The steering axle is widely used in all-wheel drive off-road vehicles.

The light-drive rear axle adopts the intubation type. The so-called intubation type is the partial casting of the intermediate bridge package. The two sides adopt the method of inserting and fixing the seamless steel pipe on both sides. The advantage is that the manufacturing process is simple and the cost is low, and the disadvantage is that the bearing capacity and precision are limited. Now gradually transition to the welding bridge
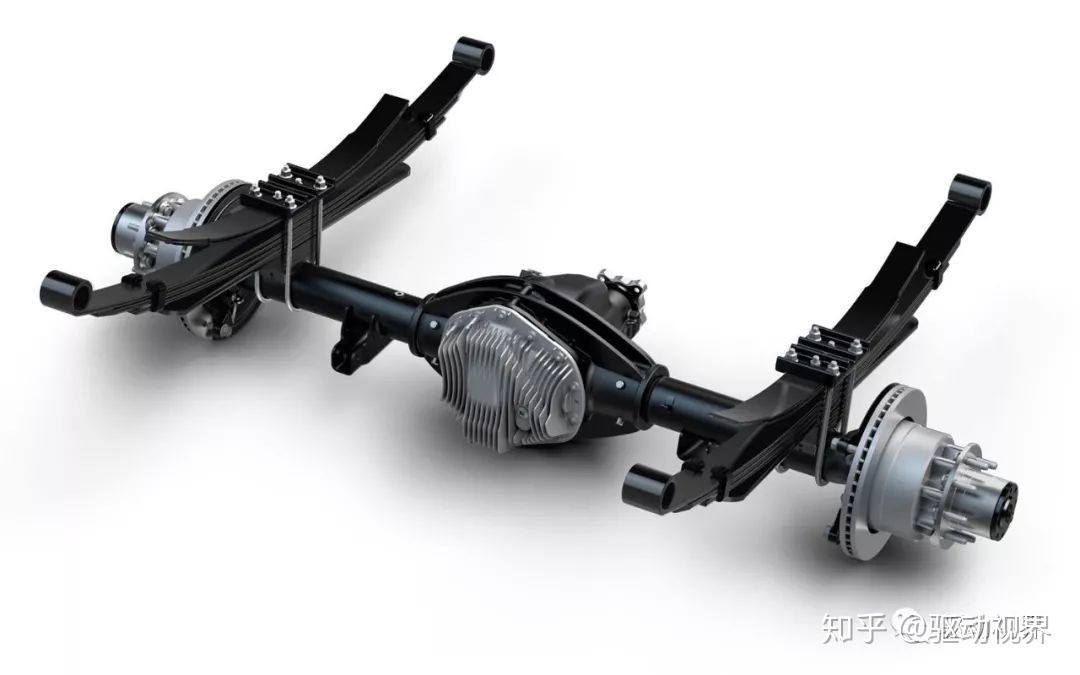

Heavy-duty single-stage deceleration bridge, only the central primary speed reducer, the axle housing is steel plate welding, the main purpose is highway logistics, no overload, requiring light weight, requiring high efficiency, due to the relatively high speed, the general axle speed More than 3-4, more matching disc brakes, hypoid gears, without differential lock.

Heavy duty single stage reduction drive rear axle

In some heavy-duty applications, there will be double rear axles, that is, through the rear axle + rear axle, the maximum load of 13Tx2
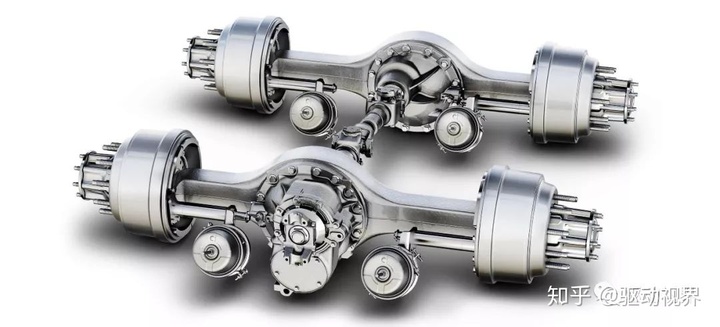
The reduction gear diameter is up to 485mm, and the current commonly used is 440/469/485
Single rear axle output torque is generally 35000Nm+

Casting double-stage bridge, casting axle housing is to improve the bearing capacity. In addition, the casting axle shell can improve the transmission precision of the axle transmission system, eliminate the deformation error caused by the steel stamping weldment, and is often used in harsh engineering applications. Improve the ground clearance, in addition to the central main reducer, also increased the wheel side secondary deceleration, the maximum load of 16Tx2
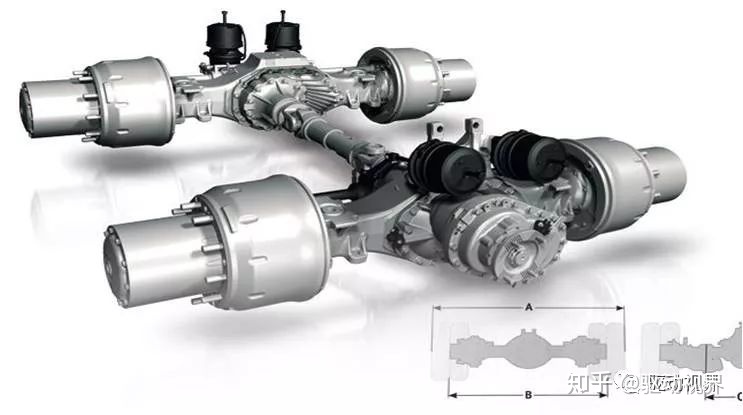
Heavy-duty wheel-side deceleration double-drive axle
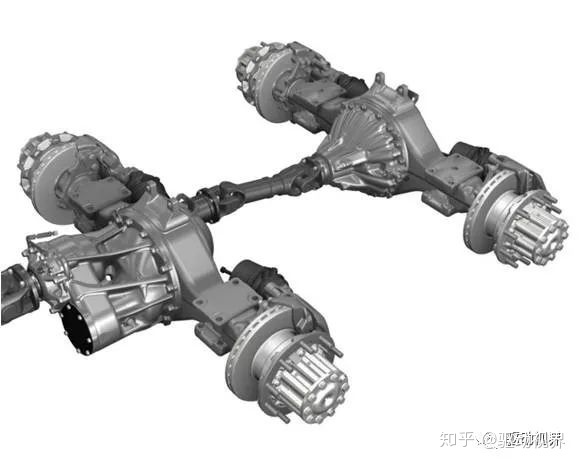

In the wheel reducer, there are two kinds of cylindrical gears and bevel gears, wherein the cylindrical gear is the mainstream.

In order to ensure the ground clearance, the diameter of the main reduction gear of the double-stage bridge is generally not more than 300mm. In order to obtain greater torque, the speed ratio is usually above 5, but the larger the speed ratio, the lower the main reduction drive gear strength, generally not exceeding 7

Single rear axle output torque can exceed 50000Nm
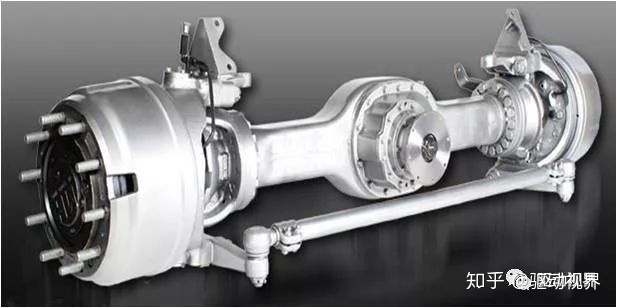
Two-stage reduction drive front axle

Two-stage reduction drive front axle
The integrated rear axle is mostly used for longitudinal powertrain models, with multiple matching leaf spring suspensions, and dual rear axle models with balanced suspension.
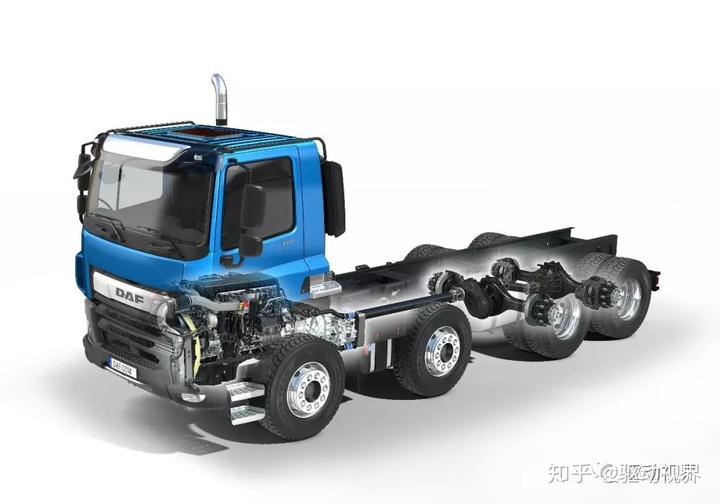

If two axles (such as the middle and rear axles of a three-axle car) are installed at the two ends of the balance bar and the middle of the balance bar is hingedly connected to the frame, one axle elevation will cause another car. The bridge is lowered.
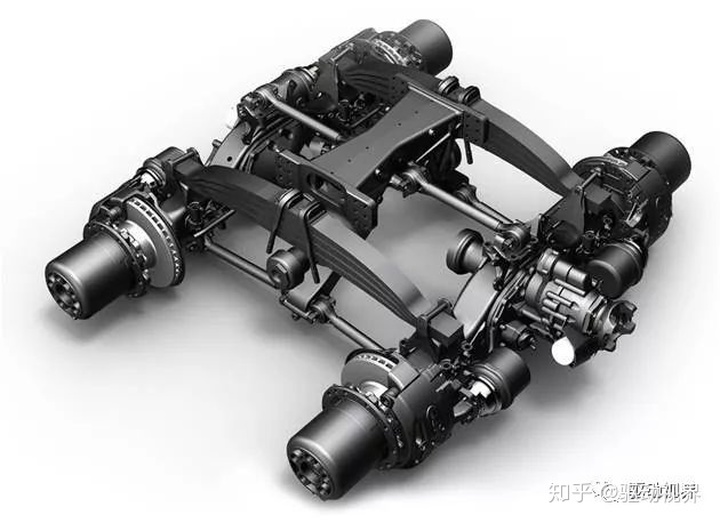

Moreover, since the balance arms are equal in length, the vertical loads of the two axles are equal in all cases, and no individual wheels are left floating. This type of suspension, which ensures that the vertical loads of the middle and rear axle wheels are equal, is called a balanced suspension.
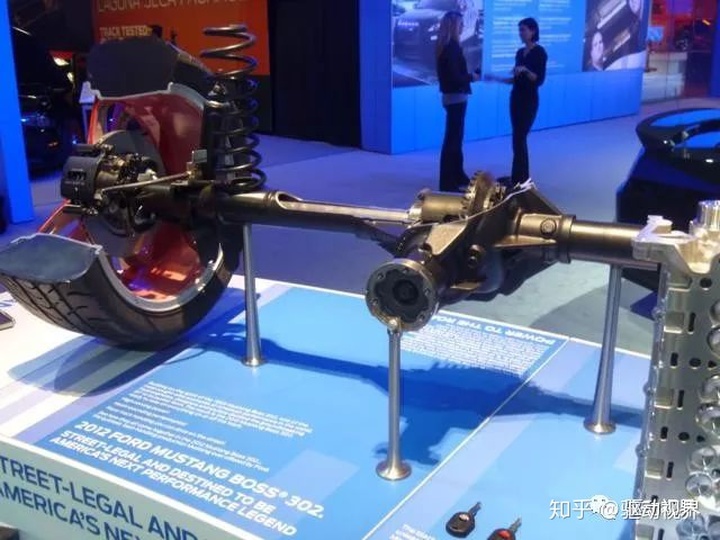

The integral light-weight drive rear axle can be matched with the coil spring in addition to the matching leaf spring. The weight of the bridge is generally less than 2 tons. The final reducer and brake are the same as the conventional bridge. The cost is low and can achieve one thousand yuan. the following

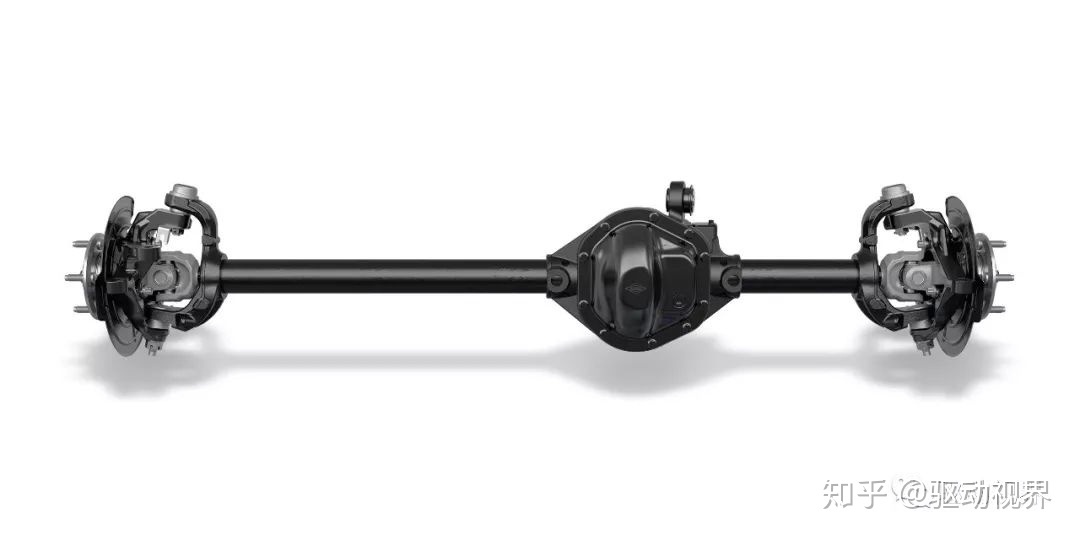
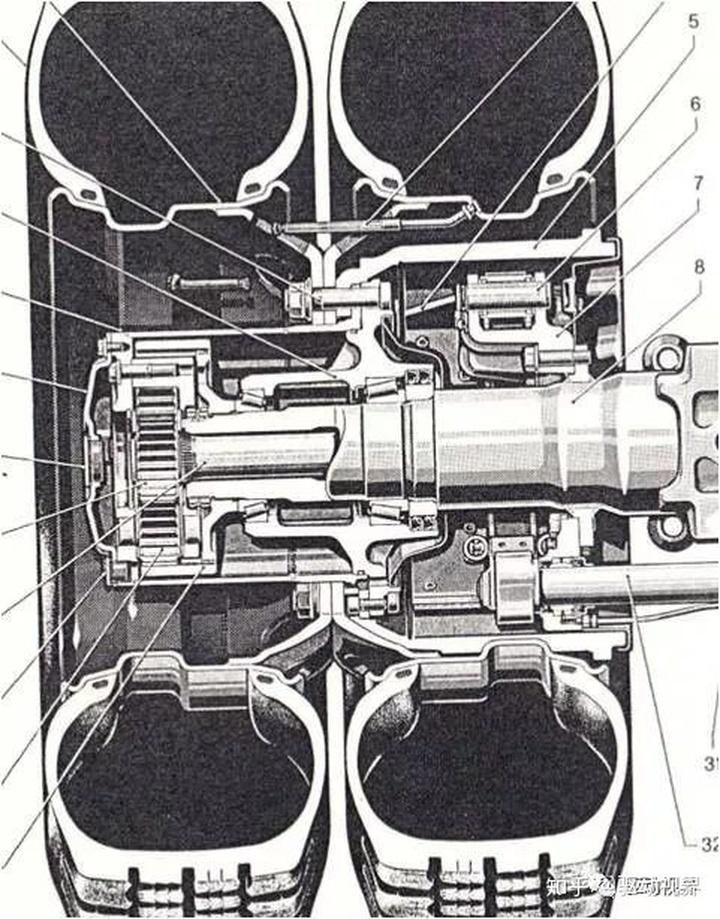
Drive axle perspective structure
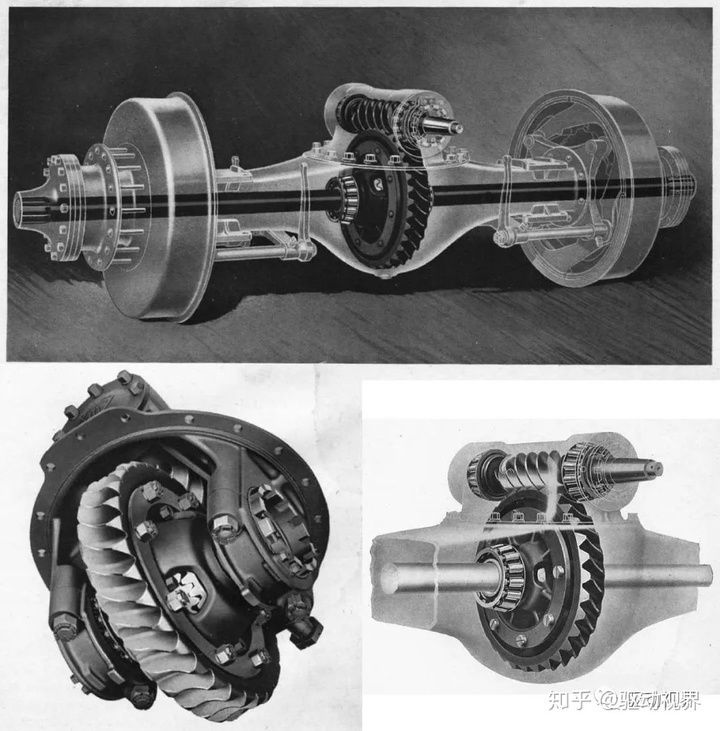
Drive axle perspective structure, worm gear structure is rare
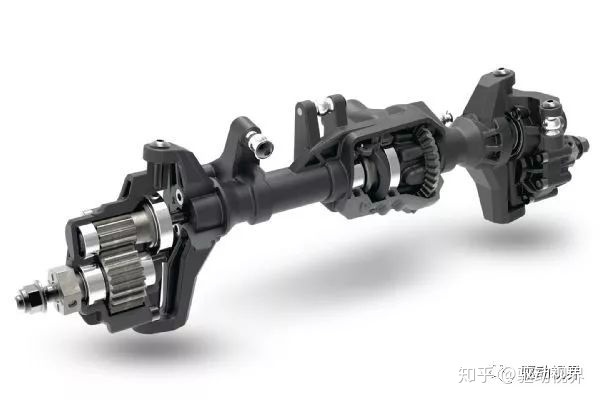

Drive axle perspective structure (door bridge)
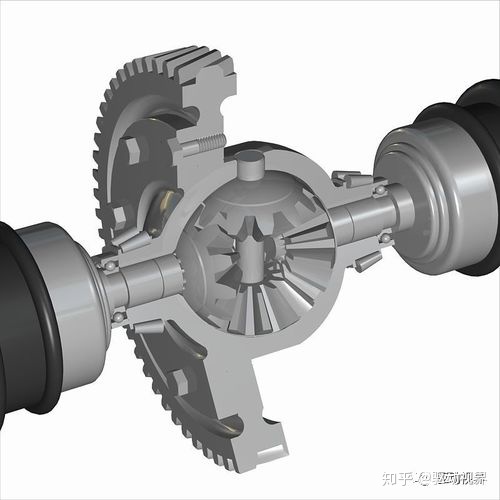
Differential
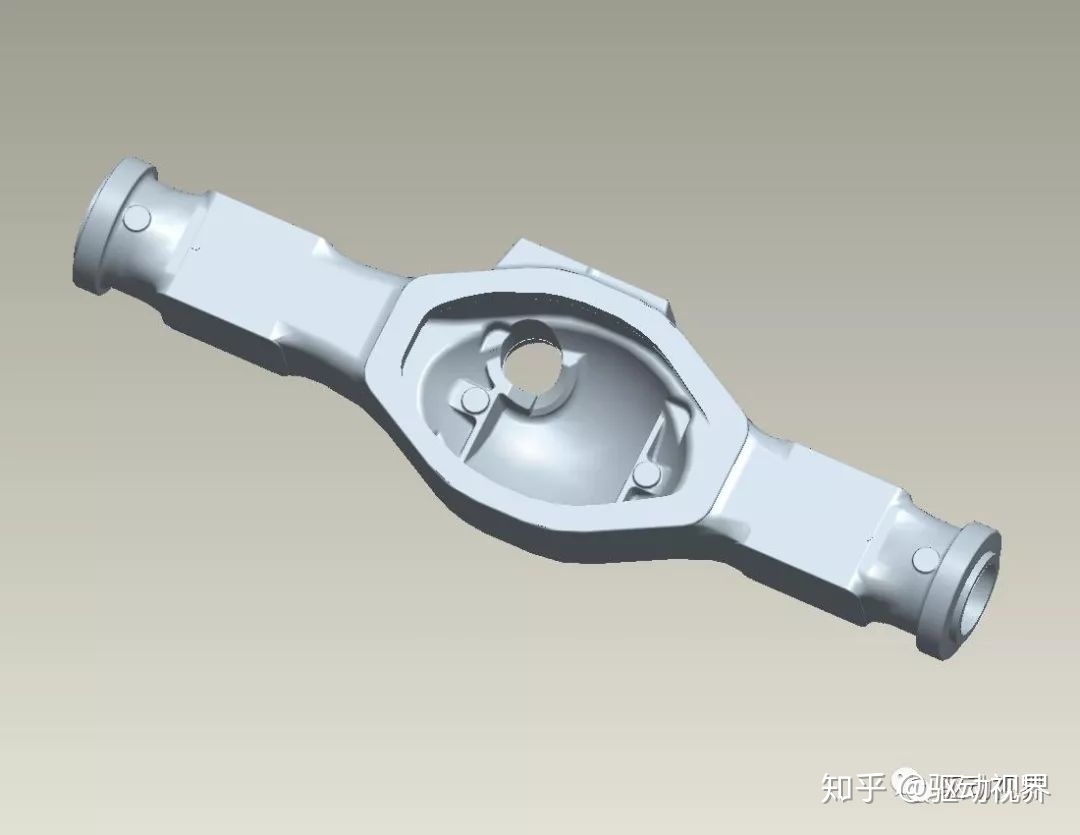

The cast monolithic axle housing can be cast from ductile iron, malleable cast iron or cast steel. A long seamless steel pipe is pressed into the semi-axial bushing at both ends of the cast monolithic axle shell and fixed with pins. On heavy trucks, To further increase the strength and rigidity of the axle housing, the back cover and the axle housing are integrally molded.
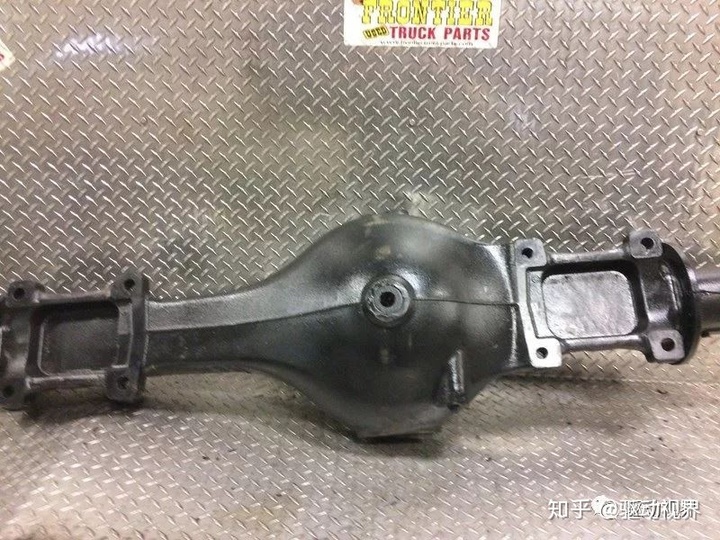

Cast axle housing

1. The bearing capacity of the cast axle housing is higher than that of the welded bridge shell.
2. The price of cast axle housing on the market is lower than that of the welded bridge shell.
3. The unit weight is large and is not suitable for lightweight transportation.
4. At present, the domestic is still the mainstream axle housing, and the parts are easy to maintain.

The stamped and welded axle housing is formed by welding a pair of axle shell main parts, a triangular steel plate, a reinforcing ring, a half shaft bushing, a back cover and a leaf spring seat, etc., between the upper and lower butt welds. The semicircular ends on both sides of the upper and lower axle shells abut against the outer circumference of the inner end of the semi-axle sleeve. In addition to welding along the seam, a plug welding process is required.

1. The thickened steel plate on the heavy-duty truck is made of steel, but the welded bridge is lighter.
2. The process requirements of steel plate welds are higher and cost than casting bridge shells.
3. Domestic axles need to be strengthened in key stress areas to ensure low failure rate.

The earliest heavy-duty welding bridge technology in China was introduced from Nissan Diesel, and Nissan Diesel Company sold the axle technology to Dongfeng and FAW. Subsequently, other domestic manufacturers have copied, this is a microcosm of the homogenization competition in the domestic axle industry."
From the manufacturer's point of view, the disadvantages of the cast axle housing are mainly the increase in self-weight and the high scrap rate. The increase in self-weight means that the load is reduced, and the waste product means waste of processing capacity. The welded bridge shell has the characteristics of high material utilization rate, low scrap rate and high productivity, which is the demand for vehicle production and development in the future.

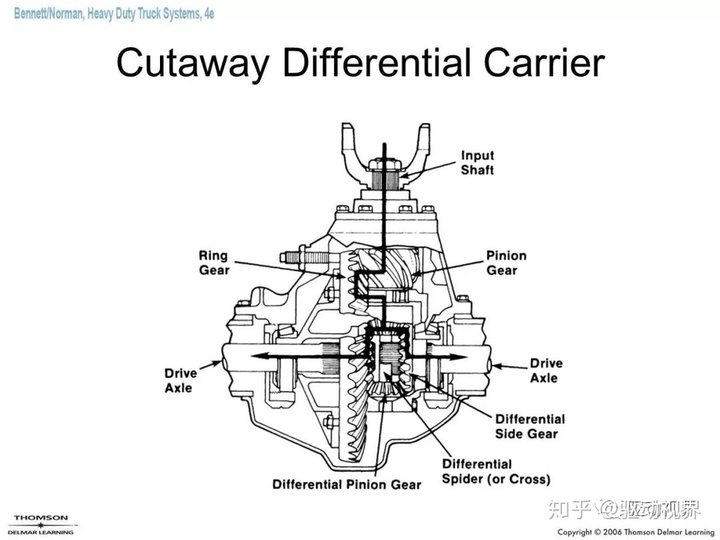
Final reduction drive A mechanism that changes torque and speed within the transaxle. The basic function is to increase the torque from the transmission or the universal transmission, while reducing the speed and changing the direction of torque transmission.
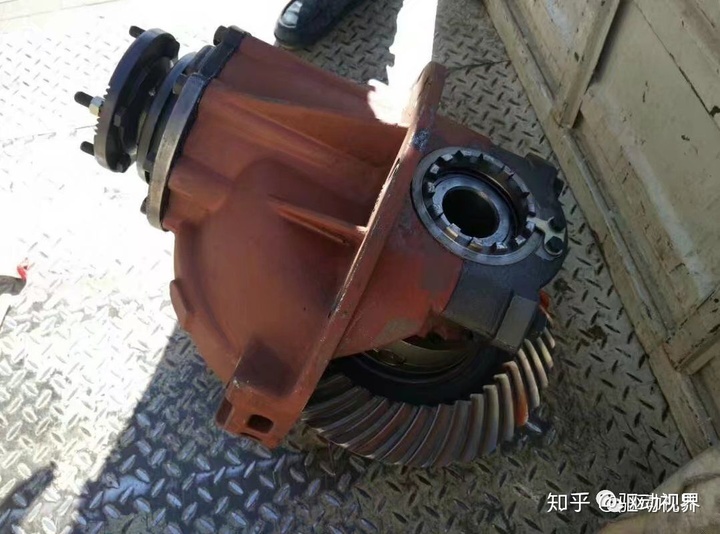

The final drive consists of one or several pairs of reduction gear pairs. The power is input by the drive gear through the driven gear. The main reducer is the main component that reduces the speed and increases the torque in the drive train. It also has the function of changing the direction of torque rotation when the engine is longitudinally positioned.
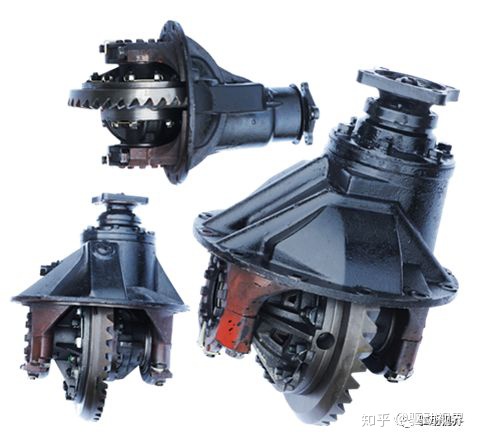

It relies on gears with a small number of teeth and a large number of gears to achieve deceleration. The use of a bevel gear transmission can change the direction of torque rotation. Arranging the final drive at a position prior to the diversion of power to the drive wheels facilitates reducing the torque transmitted by the transmission components (such as clutches, transmissions, drive shafts, etc.) in front of them, thereby reducing the size and quality of these components.

When the car is running normally, the engine speed is usually around 2000 to 3000r/min. If such a high speed is reduced by the gearbox only, the gear ratio of the gear pair in the gearbox needs to be large, and the transmission of the gear pair is large. The larger the ratio, the larger the radius ratio of the two gears, in other words, the larger the size of the gearbox.
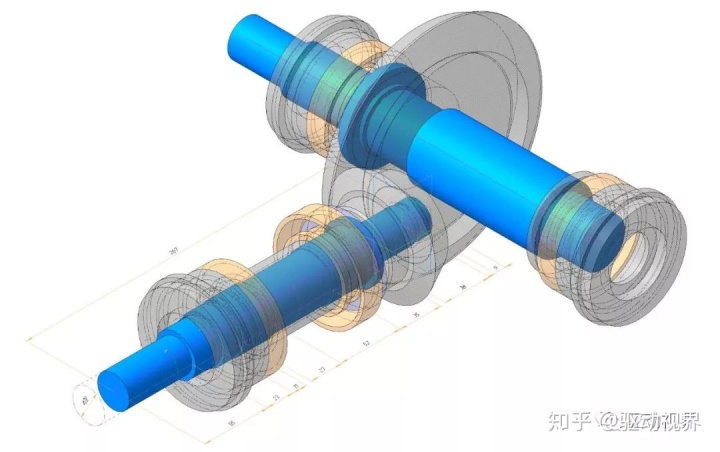
In addition, the speed is reduced, and the torque is inevitably increased, which increases the transmission load of the gearbox and the transmission mechanism of the rear gearbox. Therefore, a final drive is provided before the power differential to the left and right drive wheels.
The presence of the final drive has two functions, the first being to change the direction of power transmission and the second being to provide a common gear ratio for each gear as an extension of the transmission.
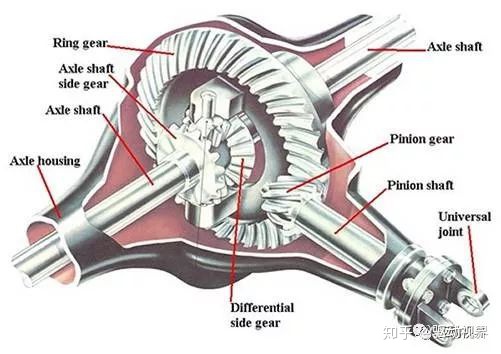
The output of the transmission is a moment that rotates about the longitudinal axis, and the wheels must rotate about the horizontal axis of the vehicle, which requires a device to change the direction of power transmission. The reason why it is called the final reducer is because the gear ratio of this device is a factor of the total gear ratio regardless of the gear position.

With this transmission ratio, the deceleration capability of the transmission can be effectively reduced. The advantage of the design is that the size of the transmission can be effectively reduced, and the overall layout of the vehicle is more reasonable.
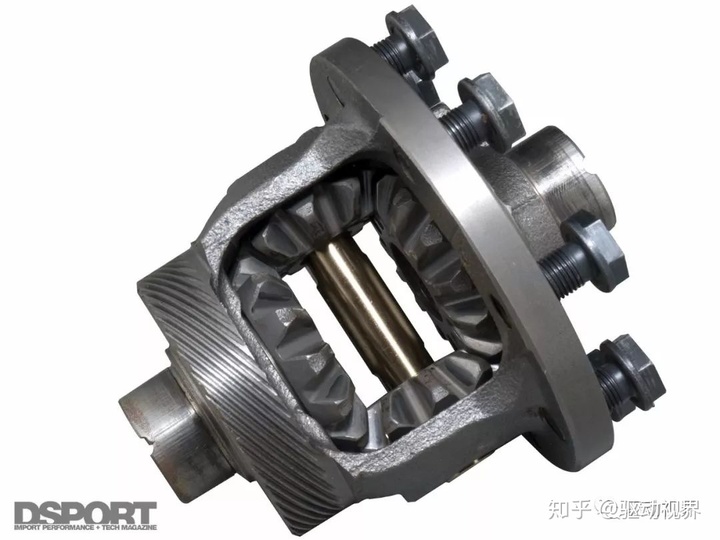

The through-type final drive has the advantages of simple structure, small mass and compact size, and can make most parts of the middle and rear axles, especially the main parts such as axle housing and semi-axle, interchangeable. .
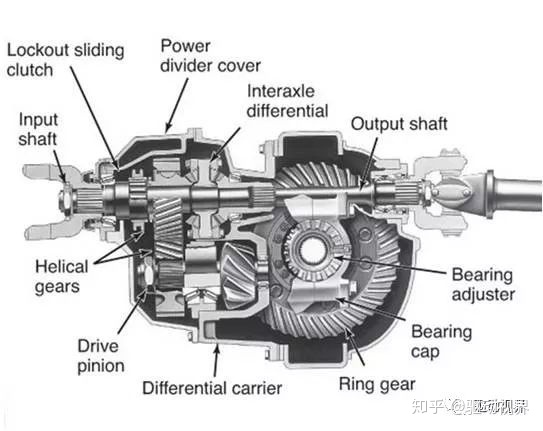
Differential lock
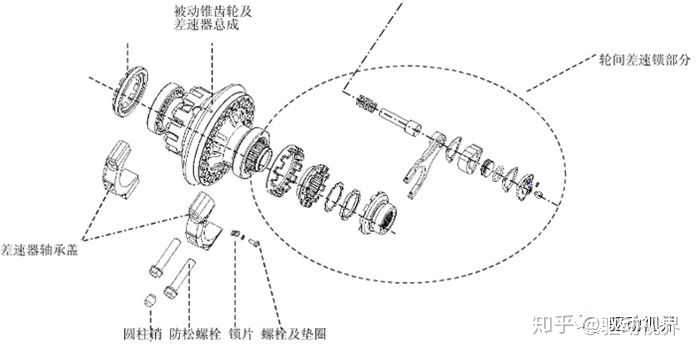
In the same time, the right wheel rolls longer than the left wheel. In order to balance the difference between the two tires, the left wheel needs to be turned a little slower, and the right wheel turns faster, using different speeds to compensate for the difference in distance.
Simply put, the role of the differential is to allow the tire to rotate at different speeds while cornering, and to eliminate wheel slip caused by various factors to maintain a consistent and smooth turn.
But nothing is omnipotent and has its advantages and disadvantages.
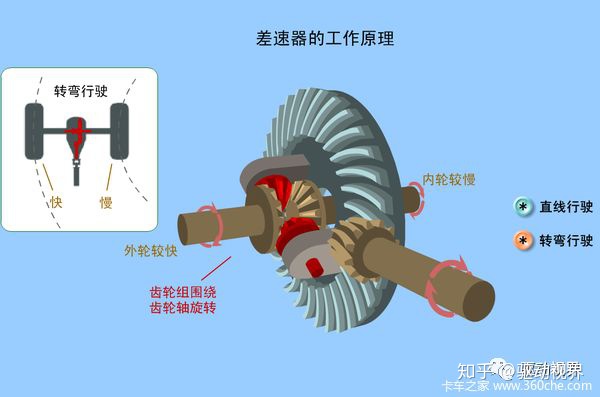
Since the differential allows the vehicle to rotate at different speeds, the differential may stupidly give most of the power to the slippery wheels when it encounters muddy slippery roads, and the other wheels lose power, causing the entire car to move.
Therefore, when the road is over muddy, slippery, etc., if one tire of the vehicle is slipping, two tires are required to maintain the same power output. At this time, the differential lock plays a key role. In short, the differential The lock is a lock that locks the differential.
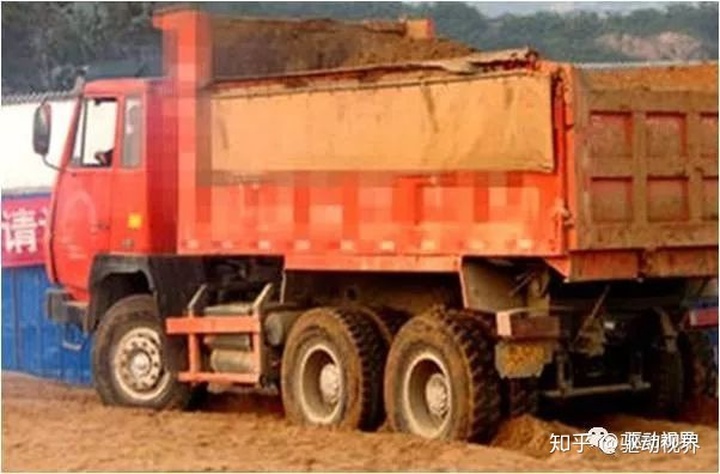

The differential lock is the "lock switch for the differential". Its function is to force the differential to be locked, so that it loses the differential effect. The two tire speeds of the same shaft or the rotational speed of each axle of the multi-axis drive vehicle are unified to increase the passing force of the vehicle on the muddy and slippery road surface.
Differential locks are classified into mechanical differential locks and electronic differential locks. On heavy trucks, mechanical differential locks are commonly used.
In the case of a heavy-duty truck with a driving form of 6x4 or 8x4, there are generally two types of differential locks between the wheel and the shaft. On some single-drive models, only the inter-wheel differential lock is available.

The inter-axle differential lock locks the differential on the through-bridge and allows the two drive axles to be hard-wired to maintain the same speed. The inter-wheel differential lock locks the differential between the wheels, allowing them to lose the differential effect and keep the left and right tires at the same speed.
When the vehicle collapses on a muddy wet road, there are generally several situations. One is that the tires on a certain axis are "fallen" and have been slipping to lose the driving force. At this time, the differential gives most of the power to the "fall" axis, and the shaft that is not "fallen" has only a small part of the power, so how can it not move. In theory, it is necessary to open the differential lock between the shafts at this time, so that the two drive axles maintain the same speed and work together to increase the passing ability of the whole vehicle. There is another situation: a tire on a certain axis "falls" and has been slipping. At this time, we need to open the differential lock between the wheels to keep the wheels on both sides at the same speed to try to get out of trouble.

The differential lock can only be engaged when the vehicle is in a stopped state. When both differential locks need to be engaged, the inter-axle differential lock should be engaged first, and then the inter-wheel differential lock should be engaged. Turning off is prohibited after the differential lock is turned on. Because the wheel speeds on both sides are not synchronized when cornering, the final drive and differential will be damaged.
After passing through the muddy wet road, the differential lock switch must be turned off in time. Note that the speed must also be zero when it is turned off.

Input flange - front through shaft - front through shaft gear - helical gear - drive bevel gear - driven bevel gear - differential case - cross shaft differential planetary gear - half shaft gear - half shaft - sun gear - planetary gear - Planetary Frame - Bell Hub - Tire Bolts - Steel Rings - Wheels
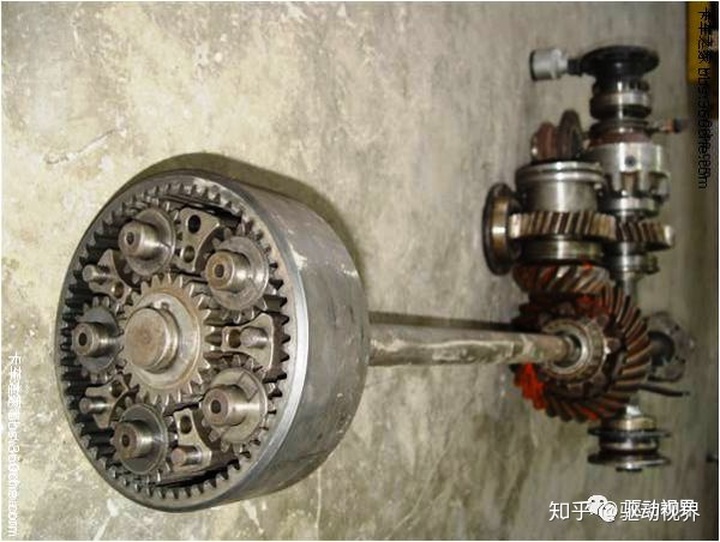

The entire drive train, Steyr Bridge
Generally speaking. The wheel reducer is used to further increase the driving force of the vehicle to meet or correct the matching of the driving force of the entire transmission system. The wheel reducer currently used is a set of gear transmissions that reduce the speed and increase the torsion to meet the needs of the entire transmission system.

From the engine through the clutch, transmission and transfer case to transfer the power to the front and rear axle final drive, and then from the output of the final drive to the wheel reducer and wheels to drive the car. In this process, the working principle of the wheel reducer is to increase the speed and torque transmitted by the final drive through its speed reduction and then transmit it to the wheel, so that the wheel will have a larger impact under the ground adhesion. Driving force.
advantage
1, through the strong
Compared with the single reducer bridge, the wheel reducer bridge is smaller than the main reducer of the single reducer bridge, and the wheel reducer bridge has a larger ground clearance, so the passability is stronger. Suitable for complex roads.
2, strong driving force
The maximum function of the wheel reducer is to reduce the speed and increase the torque, so the torque is large and the driving force is strong. Suitable for climbing
Disadvantage
1. Complex structure and low transmission efficiency
Firstly, the structure of the wheel reducer is complicated, and there are many conductive members, which causes the transmission rate to decrease and the energy loss to increase. The complicated structure makes maintenance more troublesome.
2, assembly technology requirements are high
The wheel reducer is required to be strict in the assembly process, and the dimensional deviation of the components is large, which tends to reduce the reliability of the wheel reducer. At the same time, due to the limitation of materials and structure, the heat dissipation effect of the wheel reducer in the domestic car is still It is not very ideal.
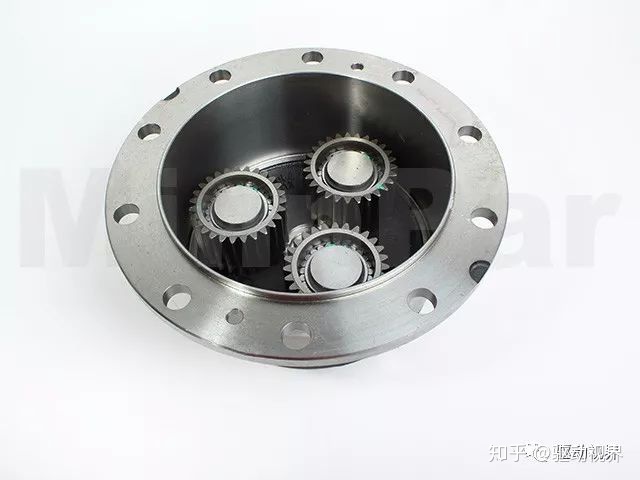


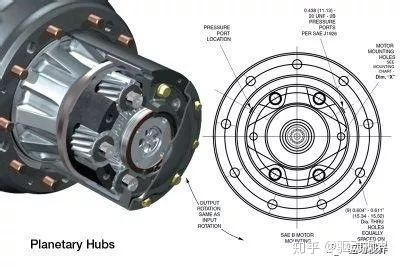
The wheel reducer is the last stage deceleration and torque increase device in the vehicle drive train. The wheel reducer can be used to make the transmission, drive shaft, final drive, differential, half shaft, etc. under the same total transmission ratio. The components have reduced load, reduced size and large ground clearance for the transaxle. They are widely used in trucks, large passenger cars, off-road vehicles and other large industrial and mining vehicles.

The wheel reducer is mainly composed of a sun gear, a planetary gear, a ring gear and a planetary carrier. Generally, the active sun gear is connected with the half shaft, the passive planetary carrier is connected with the wheel, and the ring gear is connected with the axle housing. The wheel reducer is designed to improve the driving force of the car to meet or correct the matching of the entire drive system force.
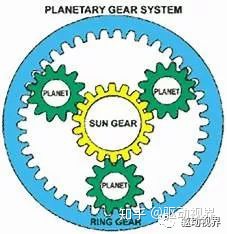
The wheel reducer currently used is a set of gear transmissions that reduce the speed and increase the torsion to meet the needs of the entire transmission system.

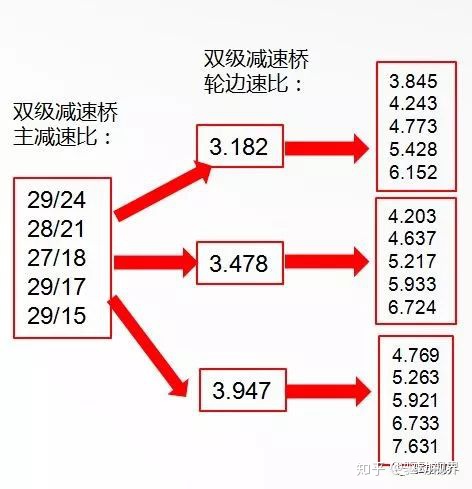
Single stage reduction bridge speed ratio
5.833 [6 to 35]
6.333[6 to 38]
6.833 [6 to 41]
5.285 [7 to 37]
4.875 [8 to 39]
4.111 [9 to 37]
4.444 [9 to 40]
3.700 [10 to 37]
3.364 [11 to 37]
3.083 [12 to 37]
2.846 [13 to 37]

With the application of low-speed and high-torque engines, the reduction of axle speed ratio is the trend

The drum brake utilizes a brake transmission mechanism to cause the brake shoe to press the brake lining against the inside of the brake drum, thereby generating a braking force, decelerating the wheel as needed or stopping in the shortest distance to ensure driving safety, and Ensure that the car is parked reliably and cannot be automatically slipped.

Drum brake

Drum brake
Wheel side
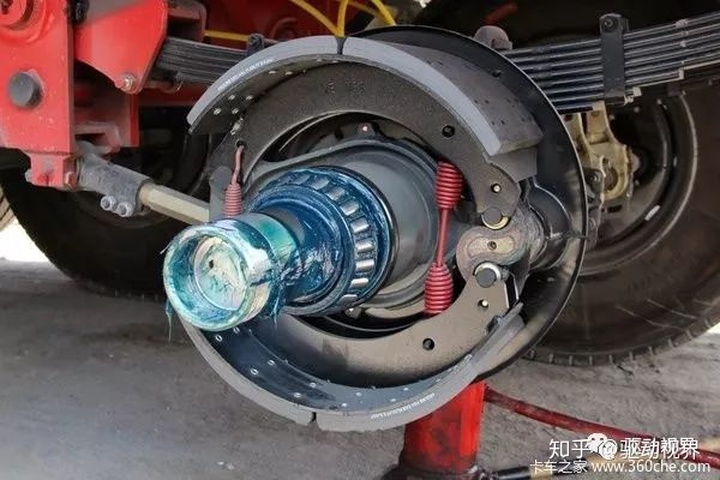

Brake and hub bearing
Braking part:
The double diaphragm spring brake chamber consists of two separate diaphragm chambers, each independently operated by a service brake and a parking brake or emergency brake element, which is used to provide braking force to the wheels.
CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
- Jining Tanzania Enterprise Cooperation Matchmaking Conference Held
- Do you know more details about friction material?
- Liangshan Shenli was selected as the champion of the 2022 municipal manufacturing single event in Jining
- Shenli company held the 4th craftsman cup theory and skill competition
- Liangshan Shenli won the honors of "Shandong famous brand" and "advanced enterprise" again
CONTACT US
Tel: +86-13792366477
Mobile: +86-13792366477
E-mail: James@chinaaxle.cn
Add: West Section of Gongming Road, Liangshan County, Jining City (Economic Development Zone)